The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is launching the Hospital Sepsis Program Core Elements to support all U.S. hospitals in ensuring effective teams and resources are in place to be able to quickly identify sepsis and save more lives. This resource is intended to help hospitals implement, monitor and optimize sepsis programs and improve survival rates. CDC’s latest survey of 5,221 hospitals found 73 percent report having sepsis teams, but only half (55 percent) report that team leaders are provided with dedicated time to manage sepsis programs.
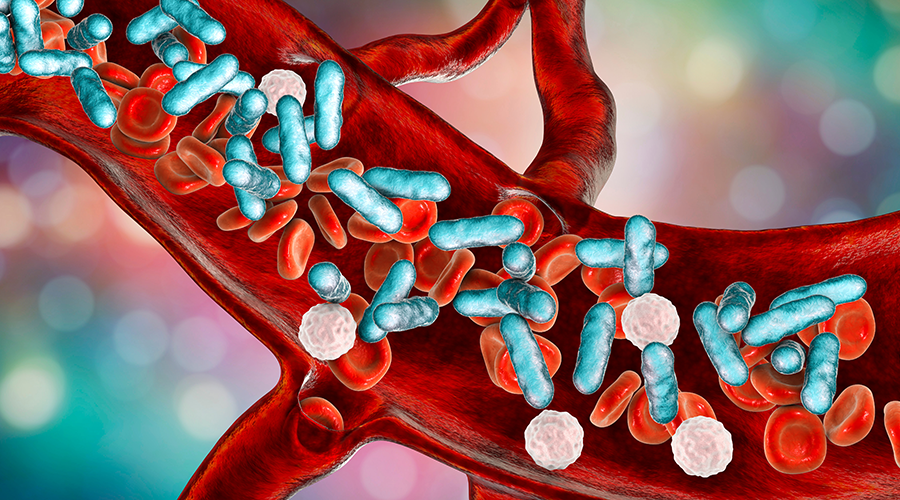
Sepsis is the body’s extreme response to an infection. It is a life-threatening condition that requires urgent medical care to prevent tissue damage, organ damage and death. In a typical year, at least 1.7 million adults in America develop sepsis and at least 350,000 adults who develop sepsis die during their hospitalization or are moved into hospice care. Most adult patients with sepsis (87 percent) are brought to the hospital with an infection that is not getting better and almost any infection, including COVID-19, influenza or RSV, can lead to sepsis.
The Sepsis Core Elements are intended to be a “manager’s guide” to organizing staff and identify the resources that will help bring sepsis rates down and survival rates up. Sepsis care is complex. The Sepsis Core Elements approach is a step to help hospitals structure their sepsis programs to coordinate multiple departments and disciplines and effectively manage the multifaceted care needed. Based on CDC’s 2022 National Healthcare Safety Network Annual Survey of hospitals, only half (55 percent) report that they integrate Antibiotic Stewardship Programs, for example, to monitor and review antibiotic and antifungal use in sepsis care. This presents an opportunity to improve a vital component of a patient’s successful recovery from sepsis.
Modeled after CDC’s Core Elements of Antibiotic Stewardship, the Sepsis Core Elements were created with the expectation that all hospitals, regardless of size and location, would benefit from this resource and incorporate the following elements into the foundation of a strong sepsis program:
- Leadership Commitment: Dedicating the necessary human, financial and information technology resources.
- Accountability: Appointing a leader responsible for program outcomes and setting concrete program goals.
- Multi-professional expertise: Engaging key partners throughout the organization.
- Action: Implementing structures and processes to improve the identification of, management of and recovery from sepsis.
- Tracking: Measuring sepsis epidemiology, outcomes, progress toward program goals and the impact of sepsis initiatives.
- Reporting: Providing usable information on sepsis treatment and outcomes to relevant partners.
- Education: Providing sepsis education to healthcare professionals during onboarding and annually.
 UF Health Hospitals Rely on Green Globes to Realize Their Full Potential
UF Health Hospitals Rely on Green Globes to Realize Their Full Potential How Healthcare Facilities Can Be Truly Disaster-Resilient
How Healthcare Facilities Can Be Truly Disaster-Resilient TriasMD Breaks Ground on DISC Surgery Center for San Fernando Valley
TriasMD Breaks Ground on DISC Surgery Center for San Fernando Valley Bigfork Valley Hospital Falls Victim to Data Breach
Bigfork Valley Hospital Falls Victim to Data Breach AI-Driven Facilities: Strategic Planning and Cost Management
AI-Driven Facilities: Strategic Planning and Cost Management