Researchers are saying that, from an infection control perspective, C. auris acts more like a multidrug-resistant, healthcare-associated bacteria than like a typical yeast, according to an article on the MedPage website.
"It is a new bug using old tricks mastered by some well-known, multidrug resistant organisms," they said.
Identifying, treating, and preventing Candida auris is a challenge facing more and more healthcare settings.
Findings presented at the 2019 ASM Microbe meeting in San Francisco by researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that patients with C. auris appear to "shed" the pathogen from their skin into their environment, which could potentially play a factor in transmission.
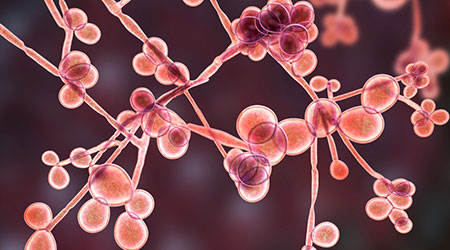
 Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris
Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens
Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach
Insight Hospital and Medical Center Falls to Data Breach The High Cost of Healthcare Violence
The High Cost of Healthcare Violence EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments
EVS Teams Can Improve Patient Experience in Emergency Departments