A study has demonstrated an association between antimicrobial resistance and climate change, according to an article on the Earth.com website.
Antimicrobial resistance was first linked to climate change when researchers noticed that resistance increased as temperatures warmed in the U.S.
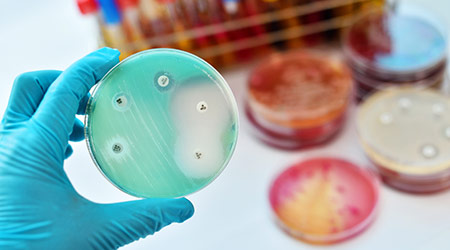
The study looked at 30 countries across Europe and found a widespread, six-year-long presence of carbapenem resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (CRPA), Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP), multiresistant Escherichia coli (MREC), and Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
The then looked at the correlation between AMR and seasonal temperatures in each region, considering potential healthcare and socioeconomic factors.
 What Does Light Daily Cleaning Miss in Patient Rooms?
What Does Light Daily Cleaning Miss in Patient Rooms? Smart Lighting Overhaul Boosts Efficiency, Diagnostics and Wellness at Bryan Health
Smart Lighting Overhaul Boosts Efficiency, Diagnostics and Wellness at Bryan Health AdventHealth Opens New Freestanding ER in Florida
AdventHealth Opens New Freestanding ER in Florida Dirty Floors: How Pathogens Can Accumulate and Spread Underfoot
Dirty Floors: How Pathogens Can Accumulate and Spread Underfoot WellSpan Health Opens Its Newberry Hospital in Pennsylvania
WellSpan Health Opens Its Newberry Hospital in Pennsylvania