Multiple recurring Clostridium difficile infections increased 189 percent from 2001 to 2012, according to an article on the Becker's Infection Control & Clinical Quality website.
In contrast, the incidence of C. diff infections rose by about 43 percent.
Researchers labeled the C. diff infections as "multiple recurrent" when the patients were teated with three courses of antibiotics, with little time between each course.
The study suggested the findings indicate multiple recurring C. diff infections place an increased burden on the healthcare system.
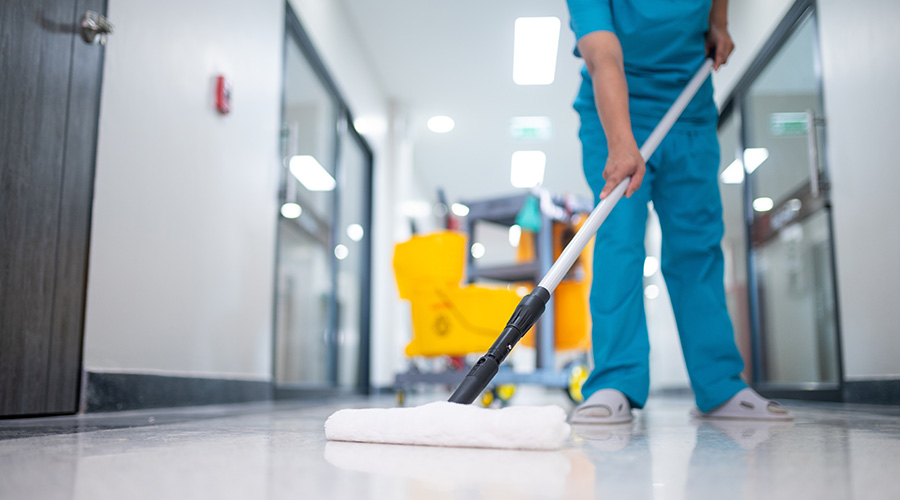
 Dirty Floors: How Pathogens Can Accumulate and Spread Underfoot
Dirty Floors: How Pathogens Can Accumulate and Spread Underfoot WellSpan Health Opens Its Newberry Hospital in Pennsylvania
WellSpan Health Opens Its Newberry Hospital in Pennsylvania Cahaba Center for Mental Health Ensnared in Data Breach
Cahaba Center for Mental Health Ensnared in Data Breach Reframing the Construction Manager as a Community Manager
Reframing the Construction Manager as a Community Manager Health First Celebrates 'Topping Off' Ceremony for New Cape Canaveral Hospital Campus
Health First Celebrates 'Topping Off' Ceremony for New Cape Canaveral Hospital Campus