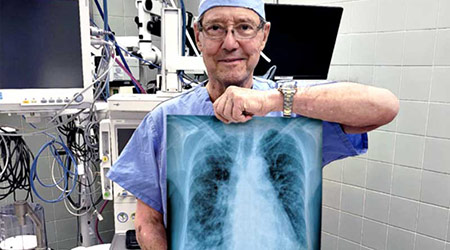
After years of inhaling surgical plume, an orthopedic surgeon in Phoenix, Ariz., was diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and underwent a double lung transplant, according to an article on the Outpatient Surgery website,
He attributes his condition to the effects of the surgical smoke.
Surgical smoke includes roughly 150 chemicals, including 16 EPA priority pollutants, toxic and carcinogenic substances, viruses and bacteria, the article said.
Smoke evacuation devices can alleviate the dangers, according to the surgeon, but not all ORs are equipped. A 2011 study, found that less than half of healthcare workers surveyed reported using local exhaust ventilation during laser surgery and only 15 percent reported local exhaust ventilation was used during electrosurgery.
 Reframing the Construction Manager as a Community Manager
Reframing the Construction Manager as a Community Manager Health First Celebrates 'Topping Off' Ceremony for New Cape Canaveral Hospital Campus
Health First Celebrates 'Topping Off' Ceremony for New Cape Canaveral Hospital Campus The University of Hawai'i Cancer Center Caught Up in Cyberattack
The University of Hawai'i Cancer Center Caught Up in Cyberattack Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris
Mature Dry Surface Biofilm Presents a Problem for Candida Auris Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens
Sutter Health's Arden Care Center Officially Opens