By: Jeannine Wang, PE LC, Director, Technology Solutions - Acuity Brands Lighting
Interest has peaked over the past year in investigating how ultraviolet light (UV) technology can be used more readily as part of an overall, more robust disinfection program. Healthcare facility managers and maintenance and facilities executives in particular are searching for more methods to keep common areas such as lobbies and waiting areas, offices, cafeterias, hallways, restrooms, and other high traffic sections safer for workers, patients and visitors.
How UV lighting works as a disinfection technology depends upon the wavelength(s) being employed. The UVC band with a wavelength of 200-280nm (nanometers) has emerged as a viable solution for interior settings such as offices, retail pharmacy settings, schools, and healthcare facilities, due to its proven effectiveness against both bacteria and viruses.
Also, UVC is straightforward to apply in a defined area and its predicted effectiveness can be predetermined within a set of application design parameters and in reference to measured output data and laboratory test data. When an adequate dose is applied, UVC light can treat an area quickly. Utilizing UVC light disinfection technology can reduce the amount of chemicals that need to be used for disinfection purposes.
When evaluating a space for application of a UV disinfection solution, there are several UVC-specific technologies to consider:
1. Intense Room Disinfection Technology (using 254nm UVC wavelength) and Upper Room Disinfection Technology (using 254nm UVC wavelength)
In general, UV technology solutions that use the 254nm UVC wavelength work well. This wavelength can effectively inactivate many common viruses and bacteria and it can be cost-effective to implement. This UV technology solution usually works with legacy fluorescent luminaires (and newer LED lighting systems).
The 254nm Intense Room Disinfection approach cannot be used in a space while occupied due to concerns over injuries that can be caused by exposure of human skin and eyes to the 254nm UVC. Typically, this technology application would be used in the evening time or during off hours of room usage, in an hour-plus-long dose, to help inactivate pathogens in the room.
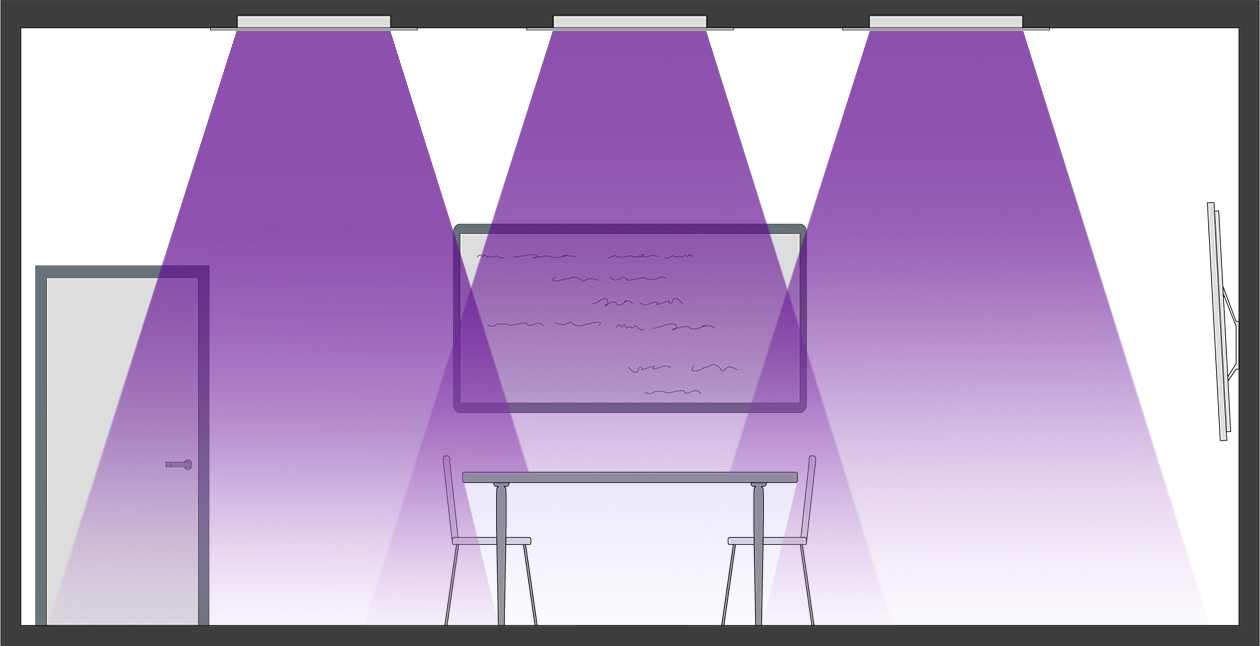 Intense Room Disinfection Technology
Intense Room Disinfection Technology
Spaces:Operating rooms, exam rooms, laboratories, restrooms, gym workout rooms, breakrooms and other high touch areas that can be treated while occupants are not present.
For the Upper Room Air Disinfection approach using 254nm UVC lamps, the UV light is aimed toward the ceiling, helping to treat the air that is circulating through the room. Although the UV light addresses the circulating air above the occupants’ heads, it does not treat any of the surfaces below eye level in the space. While this technique does allow for the system to operate while occupants are present, assuming a 9 ft. ceiling height or higher, additional caution during commissioning is imperative to make sure any occupants are protected against UV overexposure from either direct or reflected 254nm UVC light. This approach is generally less obtrusive than the Intense Room Disinfection (254 nm) approach, but it is often more expensive on per-square-foot basis in comparison.
Spaces:Waiting rooms, medical clinics, patient and visitor gathering spaces, gym workout rooms, cafeterias, large meeting areas, and other high touch areas that can be treated while occupants are present.
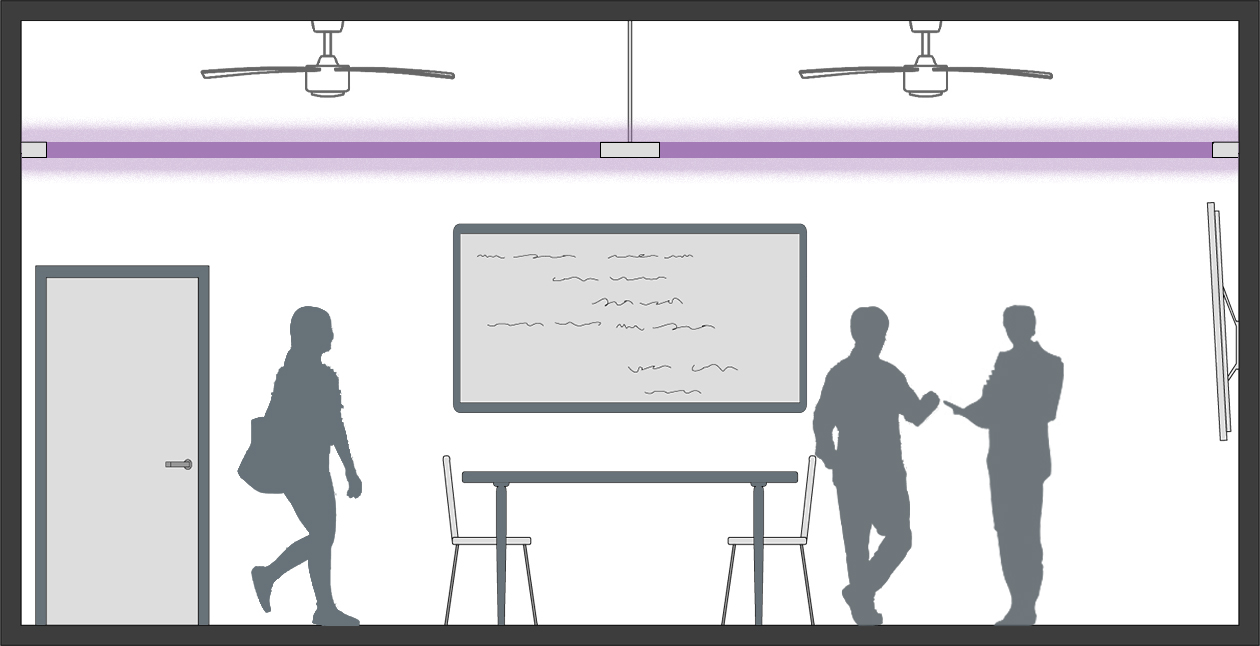 Upper Room Disinfection Technology
Upper Room Disinfection Technology
2. Intense Room Disinfection Technology (using pulsed xenon lamps)
Another solution is the Intense Room Disinfection approach using pulsed xenon-based technology, which is a relatively new type of UV disinfection technology. This approach is similar to the Intense Room Disinfection solution using 254nm UVC light, but is not as obtrusive when not in use, as the technology fits more easily into various fixtures and spaces. The pulsed xenon lamps have wavelengths ranging from 200nm up to 1,000nm, and they are exceptionally powerful. With the broad band coverage in UVA, UVB and UVC bands and high output, pulsed xenon is very fast-acting (typically used in a 30-minute cycle time) against many pathogens. Solutions that use pulsed xenon lamps can be considered for unoccupied spaces only.
 Intense Air & Surface Disinfection Technology (Pulsed Xenon - Broad Spectrum)
Intense Air & Surface Disinfection Technology (Pulsed Xenon - Broad Spectrum)
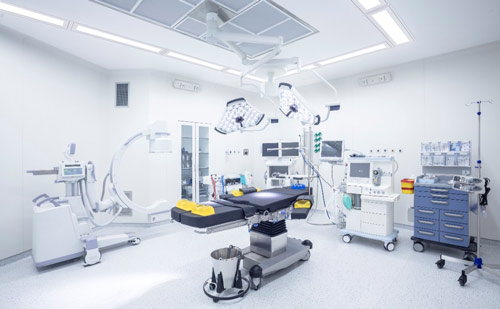 Application image of PulseX™ with Violet Defense® Technology for intense surface and air disinfection with pulsed xenon lamps
Application image of PulseX™ with Violet Defense® Technology for intense surface and air disinfection with pulsed xenon lamps
Spaces: Operating rooms, exam rooms, laboratories, restrooms, gym workout rooms, breakrooms and other high touch areas that can be treated while occupants are not present.
3. Continual Room Disinfection Technology (using filtered 222nm UVC) and Luminaire Onboard Air Disinfection Technology (using concealed 254nm lamps).
A third approach to UV disinfection incorporates the filtered far-UVC light (222nm wavelength) in a Continual Room Disinfection solution. A primary difference in this approach is that laboratory studies suggest that filtered 222nm far-UVC does not pose a health risk for human eyes and have shown that this wavelength does not pose a health risk to human skin when used within appropriate parameters, which allows it to be applied throughout the day and night in occupied or unoccupied spaces for continual reduction of active pathogens.
To clarify, it is continual active pathogen reduction and not continuous, meaning that this technology application can be turned on and off every few minutes on a regular cadence so as to remain within published UV Threshold Limit Value guidelines while providing ongoing active pathogen reduction. For example, every six minutes or every twelve minutes this type of UVC light can be applied and occupants can have the freedom to work throughout that space at any time of day or night.
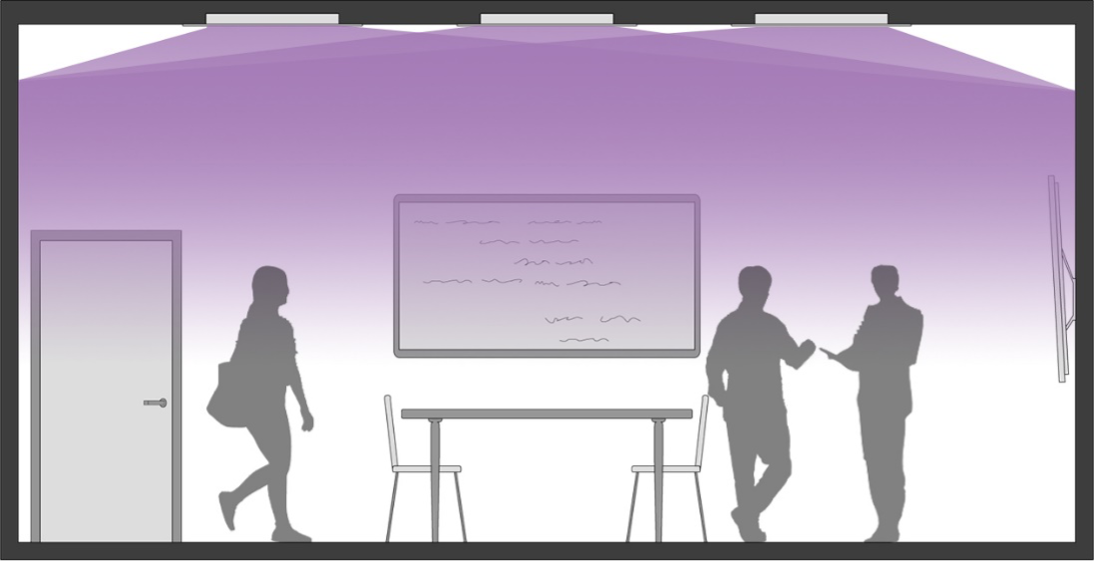 Continual Air & Surface Disinfection Technology (222nm)
Continual Air & Surface Disinfection Technology (222nm)
Finally, Luminaire Onboard Air Disinfection technology is an offshoot of the 254nm Upper Room solutions that provides a more targeted approach. It uses an enclosed fixture to take in air from the immediate surrounding area and run it through its own filtration with a 254nm lamp with UV emissions fully contained inside. The luminaire then pushes that treated air back into the room. This approach is more localized to where pathogens are potentially introduced into a space. Therefore, it is able to treat the air and turn it over numerous times per hour right in the space where the occupants are located. Occupants are not directly exposed to the 254nm wavelength in this solution.
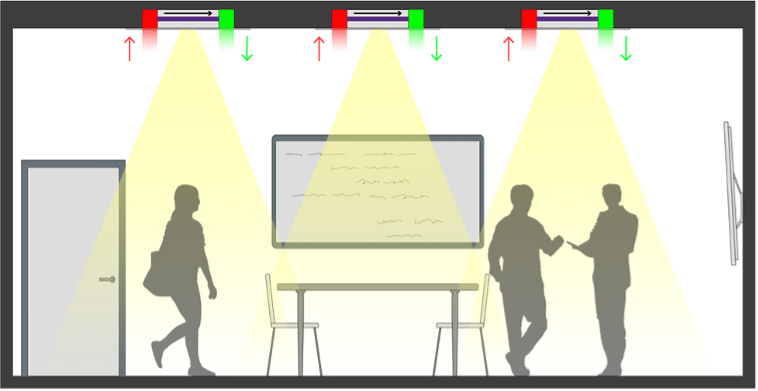 UV Onboard Air Disinfection Technology
UV Onboard Air Disinfection Technology
 Application of EvōlAir UV™ with UV Angel Clean Air™ Technology for onboard air disinfection
Application of EvōlAir UV™ with UV Angel Clean Air™ Technology for onboard air disinfection
Spaces: Waiting areas, patient and exam rooms, offices, conference rooms, restrooms, cafeterias, pharmacy retail, and other high-occupancy spaces while occupants are present.
While UV technology offers effective solutions for reducing active pathogens in healthcare spaces, it is not a perfect solution. It can do a lot of the heavy lifting to reduce active pathogens, but the technology needs to be used in conjunction with chemical and mechanical cleaning disinfection protocols to help ensure thorough disinfection. And because it is not a perfect solution, there are other aspects to consider in the overall strategies for spaces that would like to use germicidal UV as a way to help manage healthcare facilities.
Please go to UV light disinfection technology for more information.

Jeannine Wang is Director, Technology Solutions for Acuity Brands Lighting and is based in Oakland, California, where she has a leading role in accelerating market adoption of cutting-edge design platforms such as OLED lighting, circadian and dynamic lighting, and UV light disinfection technology. Jeannine is a Registered Professional Engineer (PE) in California, electrical discipline, and Lighting Certified (LC) by the National Council on Qualifications for the Lighting Profession (NCQLP). Jeannine currently serves as an advisory member for the IES Photobiology Committee.
*All references to “disinfection” are referring generally to the reduction of pathogenic bioburden and are not intended to refer to any specific definition of the term as may be used for other purposes by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The disinfection technology as incorporated in Acuity Brands products is not for use as or for medical devices. Reduction of the pathogenic bioburden is a function of fixture run time, distance to the UV light source, airflow, room size and/or other factors, and the level of reduction will vary within a specific space.
